Sutureless 25+ gauge phacovitrectomy with in-the-bag IOL implantation for small intraocular foreign body extraction through clear cornea: optimizing visual recovery
Main Article Content
Abstract
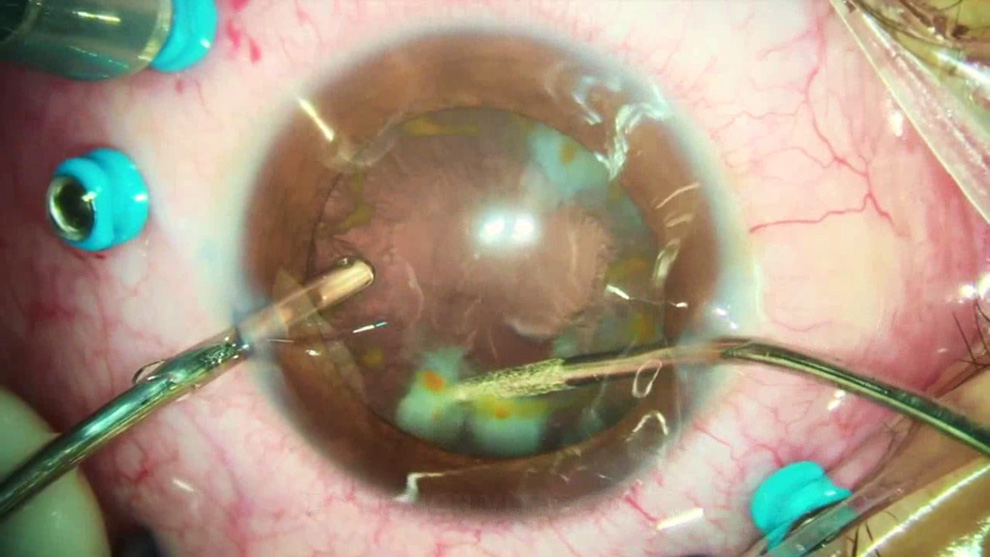
A 38-year-old man presented urgently at Clofán Clinic, Medellin, with sudden vision loss in the left eye after ocular trauma while hammering. On examination, visual acuity was light perception, there was a total cataract, and the paracentral anterior lens capsule was ruptured and had a rust-colored hue. A metallic foreign body was found within the vitreous cavity, and removal was attempted under peribulbar anesthesia in the following manner (see Video). A 2.2 mm clear corneal incision was made, facilitating cataract extraction while preserving the remaining capsular bag. This procedure was complemented by anterior vitrectomy and meticulous regularization of the posterior capsular rupture caused by the foreign body, creating a posterior circular capsulorhexis. Subsequently, a transconjunctival self-sealing three-port 25-gauge pars plana vitrectomy was performed. On identification of the foreign body, a delicate posterior vitreous detachment was induced and followed by comprehensive vitrectomy that aimed to free all surrounding tissues. Employing intraocular forceps, the foreign body was grasped perpendicular to its long axis and lifted into the anterior chamber through the posterior capsular opening. Using a precise bimanual technique with two forceps (25+ REVOLUTION DSP, serrated forceps, Alcon, Geneva, Switzerland, the foreign body was extracted through the clear corneal incision. Subsequent steps included intraocular lens (IOL) implantation within the capsular bag, a thorough retinal examination, air-fluid exchange, confirmation of ocular tone, self-sealing sclerotomies, and corneal incisions, ultimately concluding the surgery without complications. Postoperative recovery was rapid, with a final visual acuity of 20/20 without further complications.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.