“Low-fat” intradermal spindle cell lipoma of the upper eyelid: a case report
Main Article Content
Abstract
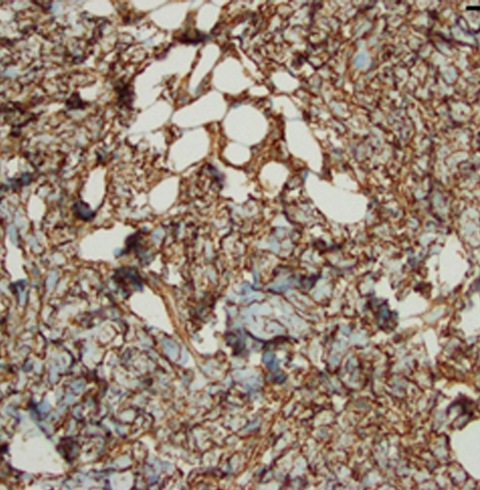
Spindle cell lipomas are slow-growing, benign tumors composed of bland spindle cells, adipocytes, and collagen bundles. They are typically found on the posterior neck, shoulder, or upper back. Spindle cell lipomas represent only a small percentage of reported lipomatous tumor types. We report the case of a 90-year-old white man who presented with a solid mobile lesion on his right upper eyelid. Histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of the lesion led to a diagnosis of a “low-fat,” intradermal, spindle cell lipoma. This case underscores the importance of considering spindle cell lipoma in the differential diagnosis for atypical eyelid lesions.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Angervall L, Dahl I, Kindblom LG, Säve-Söderbergh. Spindle cell lipoma. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A 1976;84:477-87. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00145.x
Comunoglu N, Comunoglu C, Ekici AI, Ozkan F, Dervişoglu S. Spindle cell lipoma. Pol J Pathol 2007;58:7-11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2007.05.016
Mawn LA, Jordan DR, Olberg B. Spindle-cell lipoma of the preseptal eyelid. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 1998;14:174-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00002341-199805000-00005
Charles NC, Belinsky I. “Low fat” spindle cell lipoma of the eyelid: a diagnostic challenge. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 2017;33(3S Suppl 1):S49-S51. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000000492
Fletcher CD, Martin-Bates E. Spindle cell lipoma: a clinicopathological study with some original observations. Histopathology 1987;11:803-17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.1987.tb01884.x
Pardhe N, Singh N, Bharadwaj G, Nayak PA. Spindle cell lipoma. BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2013-010438
Mariño-Enriquez A, Nascimento AF, Ligon AH, Liang C, Fletcher CD. Atypical spindle cell lipomatous tumor: clinicopathologic characterization of 232 cases demonstrating a morphologic spectrum. Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:234-44. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0000000000000770
Cheah A, Billings S, Goldblum J, Hornick J, Uddin N, Rubin B. Spindle cell/pleomorphic lipomas of the face: an under-recognized diagnosis. Histopathology 2015;66:430-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/his.12548
Ud Din N, Zhang P, Sukov WR, et al. Spindle cell lipomas arising at atypical locations. Am J Clin Pathol 2016;146:487-95. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcp/aqw137
French CA, Mentzel T, Kutzner H, Fletcher CD. Intradermal spindle cell/pleomorphic lipoma: a distinct subset. Am J Dermatopathol 2000;22:496-502. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00000372-200012000-00003
Rubin BP, Fletcher CD. The cytogenetics of lipomatous tumours. Histopathology 1997;30:507-11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2559.1997.5680797.x
Lincoln M, Royer M. Uncommon tumor, uncommon location: a dermal-based spindle cell/pleomorphic lipoma. Am J Dermatopathol 2016;38:e122-4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/DAD.0000000000000546
Hornick JL BJ. Sternberg’s Diagnostic Surgical Pathology. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health; 2015.
Sidney LE, Branch MJ, Dunphy SE, Dua HS, Hopkinson A. Concise review: evidence for CD34 as a common marker for diverse progenitors. Stem Cells 2014;32:1380-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1661
Mandahl N, Mertens F, Willén H, Rydholm A, Brosjö O, Mitelman F. A new cytogenetic subgroup in lipomas: loss of chromosome 16 material in spindle cell and pleomorphic lipomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 1994;120:707-11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01194267
Chen BJ, Mariño-Enríquez A, Fletcher CD, Hornick JL. Loss of retinoblastoma protein expression in spindle cell/pleomorphic lipomas and cytogenetically related tumors: an immunohistochemical study with diagnostic implications. Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1119-28. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0b013e31825d532d
Billings SD, Folpe AL. Diagnostically challenging spindle cell lipomas: a report of 34 “low-fat” and “fat-free” variants. Am J Dermatopathol 2007;29:437-42. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/DAD.0b013e31813735df
Ohshima Y, Nishio J, Nakayama S, Koga K, Aoki M, Yamamoto T. Spindle cell lipoma and pleomorphic lipoma: an update and review. Cancer Diagn Progn 2023;3:282-90. DOI: https://doi.org/10.21873/cdp.10213
Hostein I, Pelmus M, Aurias A, Pedeutour F, Mathoulin-Pélissier S, Coindre JM. Evaluation of MDM2 and CDK4 amplification by real-time PCR on paraffin wax-embedded material: a potential tool for the diagnosis of atypical lipomatous tumours/well-differentiated liposarcomas. J Pathol 2004;202:95-102. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1495
Tariq MU, Din NU, Abdul-Ghafar J, Park YK. The many faces of solitary fibrous tumor; diversity of histological features, differential diagnosis and role of molecular studies and surrogate markers in avoiding misdiagnosis and predicting the behavior. Diagn Pathol 2021;16:32. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-021-01095-2
Rodriguez FJ, Folpe AL, Giannini C, Perry A. Pathology of peripheral nerve sheath tumors: diagnostic overview and update on selected diagnostic problems. Acta Neuropathol 2012;123:295-319. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-012-0954-z
Allen A, Ahn C, Sangüeza OP. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Dermatol Clin 2019;37:483-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.det.2019.05.006
Mentzel T, Beham A, Katenkamp D, Dei Tos AP, Fletcher CD. Fibrosarcomatous (“high-grade”) dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of a series of 41 cases with emphasis on prognostic significance. Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:576-87. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00000478-199805000-00009
Zeng YF, Dai YZ, Chen M. Mammary-type myofibroblastoma with infarction and atypical mitosis-a potential diagnostic pitfall: a case report. World J Clin Cases 2022;10:5343-51. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i16.5343
Hox V, Vander Poorten V, Delaere PR, Hermans R, Debiec-Rychter M, Sciot R. Extramammary myofibroblastoma in the head and neck region. Neck 2009;31:1240-4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.20990
Howitt BE, Fletcher CD. Mammary-type myofibroblastoma: clinicopathologic characterization in a series of 143 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40;361-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0000000000000540
An S, Song JS, Park S, Lee JW, Cho KJ. Mammary-type myofibroblastoma: a report of two cases. J Pathol Transl Med 2016;50:385-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.03.26