Advanced tubercular ampiginous-like choroiditis
Main Article Content
Abstract
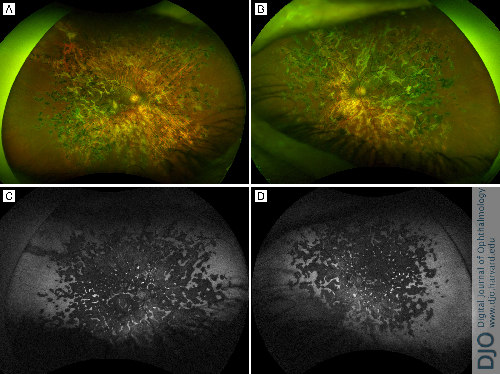
A 68-year-old white man presented at Wills Eye Hospital with chronic decreased vision in both eyes. His social history was significant for prior incarceration. Dilated fundus examination of both eyes demonstrated extensive chorioretinal scarring and fibrosis (A, B). Widefield imaging fundus autofluoresence demonstrated extensive areas of hypoautofluoresence (C, D). Infectious and inflammatory workup was significant for positive purified protein derivative and QuantiFERON-TB Gold testing. The patient was subsequently diagnosed with tubercular ampiginois-like choroiditis. In conjunction with the infectious disease service, he underwent treatment with four-drug (rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, ethambutol) therapy and oral prednisone. He was eventually transitioned to immunomodulatory therapy with methotrexate and stabilized with counting fingers visual acuity in the right eye and 20/100 in the left eye.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.