Treatment of Takayasu arteritis–related photic and postprandial amaurosis
Main Article Content
Abstract
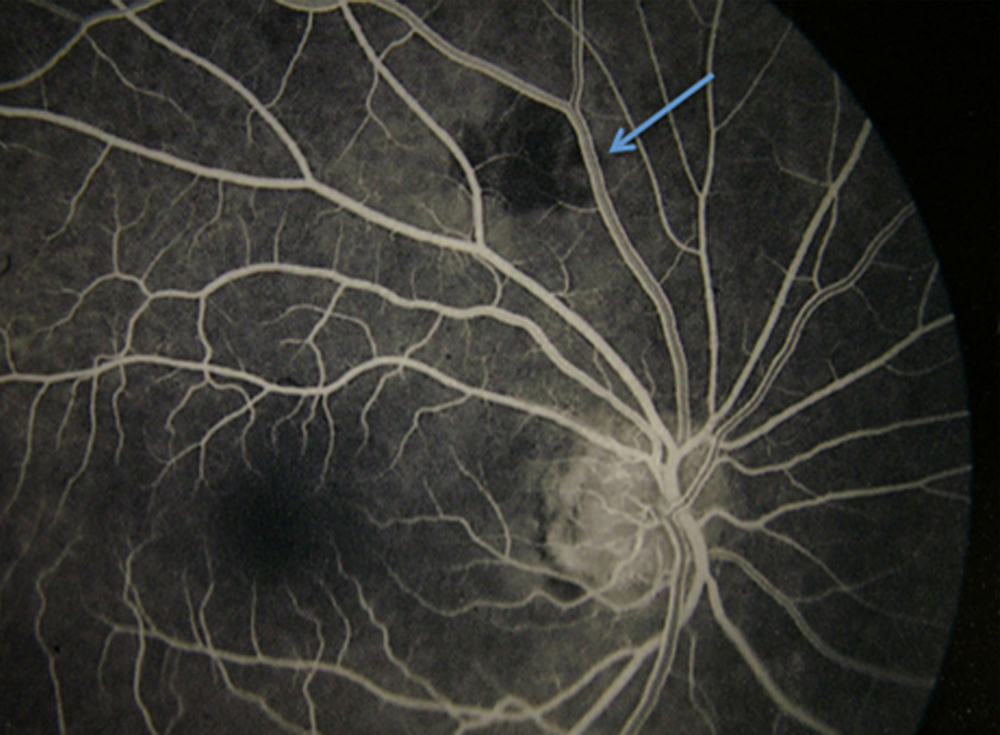
We report the case of a 66-year-old man with Takayasu arteritis who developed photic and postprandial amaurosis occurring at a corticosteroid dose <40 mg per day, despite concurrent methotrexate. The amaurosis resolved with correction of anemia by packed red blood cell transfusion. Marginal retinal perfusion in Takayasu arteritis may precipitate symptomatic hypoxia as a result of eating a meal or exposing the eye to bright lights. Correction of anemia improves oxygen delivery to the hypoxic retina and relieves recurrent amaurosis.
Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Article Details
How to Cite
1.
Wong SH, Turbin RE, Frohman LP. Treatment of Takayasu arteritis–related photic and postprandial amaurosis. Digit J Ophthalmol. 2017;23(4):104-105. doi:10.5693/djo.02.2017.09.002
Issue
Section
Case Reports

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.