Solitary retinal astrocytic hamartoma
Main Article Content
Abstract
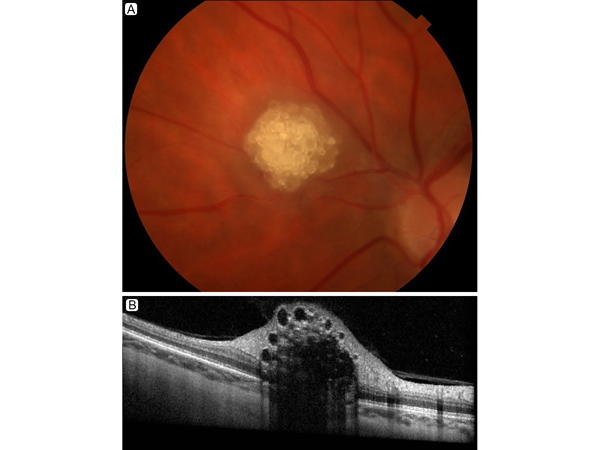
A 47-year-old woman with a past medical history of seizures was referred to Massachusetts Eye and Ear for evaluation of a retinal astrocytic hamartoma in the left eye. Her visual acuity at presentation was 20/15 in each eye. Fundus photography (A) showed a raised, multinodular, “mulberry-like” lesion. Optical coherence tomography (B) revealed a “moth-eaten,” optically empty space isolated to the nerve fiber layer. Physical examination showed no skin lesions. Brain and abdominal magnetic resonance imaging, and computed tomography of the chest showed no evidence of systemic lesions. Thus, a diagnosis of sporadic, unilateral, retinal astrocytic hamartoma was established. No intervention was needed, and an annual follow-up examination was recommended.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.